CSS Positioning
CSS positioning is what you use to position elements on a document. You can position elements behind or in front of other elements and set them inline or have them stack like block level elements. Positioning with CSS can be very complicated, but with some understanding and practice you should understand it in no time. There are several different positioning methods including:
- Static
- Relative
- Absolute
- Fixed
- Float
- Z-Index
Static Positioning – the default positioning state that html uses on a page. Static positioning positions the elements with the normal flow of the page. Static positioned elements can not be styled using the top, right, bottom, left properties.
Relative Positioning – runs off of the parent element that is positioned and then determines how to position itself from it. Relative positioning can overlap other elements, however, it will reserve the space where it would have been placed in the flow.
Absolute Positioning - looks for the parent elements positioning and positions itself off of it also. If there is no positioning for the parent element it will go all the way back to the firsttag and position itself from their. Absolute positioning lets to position an element exactly where you want it down to a pixel and is positioned by using the top, right, bottom, left attributes. Absolute is unlike relative in that it does not reserve a space for it.
Fixed Positioning – removes the element for the normal flow of elements on the page and places it like absolute positioning, except it does not moved when the user scrolls down the page. It is positioned using the top, left, bottom, right attributes and is parent to the browser.
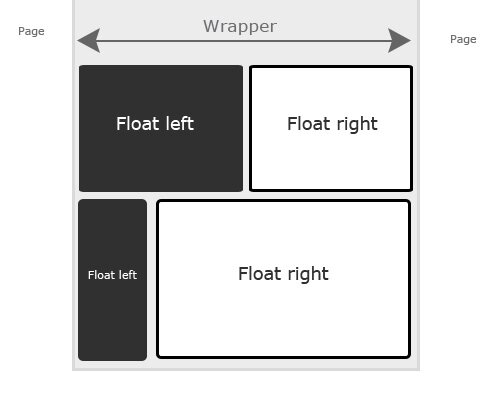
Float Positioning - is used to push an element to the left or right of a page. It cannot be used to float top and bottom. Float positioning allows other elements to wrap around it and is generally used for listing items or displaying columns on the left and right side of a document. You must use the clear: both; command to prevent the float from continuing down the document to the next element.
Z-Index Positioning – controls which element displays on top of another element. Think of this as the 3d positioning property. If you want say an image to display over the footer of your document. you would specify the z-index to be higher than the footer. if you have two elements that overlap without a z-index specified, the element positioned last will be shown on top of that item.

